You are here: |
Topic: Carbohydrates |
 |
CarbohydratesFrom the beginning Remember the periodic table in high school. This table shows the elements in order of weight starting with hydrogen. There are many elements on the periodic table and some that we are more familiar with are calcium (Ca), copper (Cu), iron (Fe) and carbon (C). Water is composed of two hydrogen's and one oxygen to make H2O. The abbreviations are: H - Hydrogen, O - Oxygen. We can hydrate our body with water. In chemistry the addition of water is called a hydrate. When a carbon is hydrated it is then called a carbohydrate. This is one carbon plus one water. Most of the carbohydrates that we know about have six carbons and six waters. Sugar contains six carbons and six waters - C6H12O6. There are three variations of the base sugars.
1. fructose, with two "tails" dissolves in water easily The terms in biology and chemistry can become like learning a new language - difficult, but necessary. In chemistry a sugar is called a saccarhide. The prefixes tell us how many sugars are present: Most sugar that we know about are in the from of di saccharides. Digestion breaks up the complex, poly and di saccarrhides into the mono saccahides. These simple sugars dissolve into blood plasma (water based) for transport and production. Digestion is the process of adding water, or hydrating molecules into single units. Our body processes sugar into what we call processed sugar. See biology and chemistry can be easy. Every cell in our body can use glucose. The amount fo glucose is like alcohol, a little can be fun but too much and we get sick. Alcohol is the fermentation of sugar, ahem, fermented saccharrides in chemistry terms. Glucose hardly ferments, Fructose ferments or accumulates as fatty liver and belly fat. Controlling which simple sugar goes where and the concentration is very important. Too much sugar is like too much alcohol; either sugar or alcohol can become toxic. Remember:
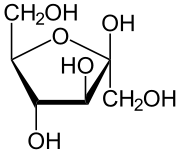
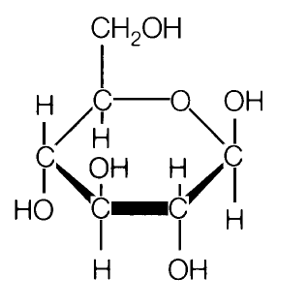
We want blood sugars for energy, but not too much. Controlling blood sugar (glucose)1. speed of digestion, the inclusion of a protein or fat which slows down digestion and also slows down sugar release into the body. Here is the kicker that most people and professionals do not understand. Only glucose can be stored in the body and cells for energy. None of the fructose sugar can be storred and cannot be used for any energy what-so-ever. Every cell in the body needs glucose and every cell in the body is harmed by fructose. The size of the liver is large to grab all fructose on first pass from digestion to empty it into the bile ducts to the bowel for elimination. Any excess causes fatty liver, fatty body, diabetes and bad cholesterol. ----------------------------- Review: The small carbohydrates are called sugar. These tend to have six carbons and six waters; C6H12O6. These six carbon sugars are called fructose, galactose and glucose. In chemistry a sugar is indicated by the suffix ose. The chemistry name for a sugar is saccarhide. The single saccarhides are called mono for one, a monosaccaride. In nature the sugars are always found in pairs. The name for two is di so a disaccaride would be a natural sugar whereas a monosaccharide is a processed sugar. The smallest carbohydrate has six carbons and six waters (C6H12O6). The small carbohydrates are called sugars. Another name for sugar is saccharides where the word saccharide means sugar. The word sugar alone does not tell us about the size of the carbohydrate, the word saccharide is easier to distinguish how big the molecule is by adding mono-one, di-two or poly-many to the front. A mono-saccharide is one sugar, the smallest and the simplest. There are three different structural arrangements of the six carbon and six water mono-saccharides called fructose, galactose and glucose. When a word ends with –ose it means that it is a sugar/saccharide. Picture of C-H-O fructose (left) and glucose (right) (aka dextrose) molecules
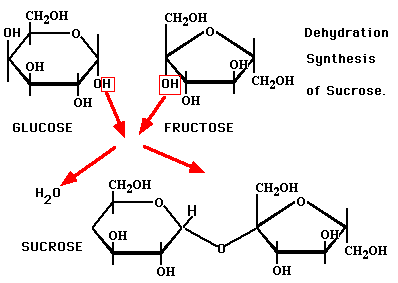
Any of these forms of simple sugars could be called a processed sugar because they do not commonly occur in nature as monosccharides. To become more stable they are often bound together with each other. When any two monsaccharides bond together chemically we call them di-saccharides. These are the sugars used in our daily lives and found in our food. We eat the disccharides but the body converts them into monosacharides by digestion, because the body can only absorb and use them as energy in this form. Sucrose, often known as table sugar is a di-saccharide of fructose bonded to glucose. Not all table sugars are the same; there are many variations in the actual ratio between the number of fructose and glucose giving us different types of sugars. In beet sugar the ratio of fructose is more than that of glucose. A table sugar made from sugar cane has less fructose and more glucose. Sucrose is always made from plant sources. A picture showing how glucose and fructose combine to make a sucrose molecule and give out a water molecule as a result (dehydration) Lactose is the scientific name for milk sugars where a galactose bonds to glucose. This is the only sugar made from animal sources and comes from the milk. It is hard to break this bond as needed in digestion. To break this bond in humans we rely on a wide range of bacteria that are often named with lacto- at the beginning. Some examples are; lacto-bibidus, lacto-acidophilus, lacto-helveticus, lacto-plantarium, lacto-casei, and many others. Most of these bacteria help our digestion and are safe for our bodies. When they are too few of them we become allergic to milk known as lactose intolerant. Taking an effective amount of the lacto-bacteria usually reverses the dairy problems. Maltose, also called malt sugar is a di-saccharide made from a glucose bonded to another glucose. This is a fermentable sugar usually formed from starch by the action of the enzyme amylase. Polysaccharides (poly-many) are groups of molecules that can be made up of a few to as many as 10,000 monosaccharides. There are many different variations of how these bonds are formed a complex way so we call them complex carbohydrates and commonly known as starches. One thing that remains the same is that all saccharides dissolve in water and they all breakdown to release the monsaccharides by the process of digestion. There are some physical differences between fructose and glucose that make them work differently in nature. One difference is that glucose (glu-glue) likes to stick to itself better than fructose. This means that sugars with a high ratio of glucose need more stirring to dissolve while sugars with a high ratio of fructose dissolve fast and easy. Another difference is that fructose tastes sweater than glucose. When used in food or as a coating fructose browns at a lower temperature (easier) than glucose. When making something like a browning sauce for roast or barbeque chicken the food industry has switched to saccharides that have a high ratio of fructose. The food producers have less stirring, less settling out of sugar crystals as sugar granules on the shelf, better sweetness per pound/kilogram and better browning properties by using fructose. The high fructose additives are sometimes called invert sugar, modified corn starch, high fructose corn syrup, apple juice, pear juice and honey. Fructose is the cause of obesity, heart disease and diabetes. After digesting carbohydrates down into mono-saccharides the blood first passes to the liver where all fructose must be removed. When the liver is overwhelmed with fructose it becomes fatty and full of holes worse than an alcoholic. If the liver fails to capture the fructose and some passes to the nerves they become burned and we develop nerve damage first in the long nerves to the feet and fingers. With this 'hot' sugar we also begin to grow tissues such as polyps, fibroids and tumors. When in the brain these can show up as many or multiple sclerosis where sclerosis means scars. Some times they show up as sarcoidosis or lumps throughout the body. Once these lumps are calcified we are in chronic problems and fructose makes them grow faster and for some people the body stops producing insulin (type 1 diabetes) or the cells begin to block the effects of insulin (type 2 diabetes). This is in response to the liver failing to capture all fructose from the blood before circulating through the body. Glucose does not do this and when two glucose molecules bind together we commonly find this in the starch of potato and rice. Honey is 80% fructose and high fructose corn syrup is often 55% fructose. Maple syrup is 33% fructose but when sick all sugars become problematic. To slow down the digestion of carbohydrates the best traditional habit was to combine the rice and potato with a full meal to include some fat and protein. This is why we put butter on potato, sour cream on perogies, cheese on pasta and peanuts with Vietnamese and Thai noodles. The Chinese start a meal with a small serving of peanuts. Better than carbohydrates Nitrogen is our FIRST and BEST source of energy, powerful as gunpowder.
Here is a study that those who consume nuts and peanuts (legumes) have significant lower rates of diabetes. See the topic diabetes for more information. Peanuts contain significant levels of arginine. Children survive without arginine in the diet but adults do not. More will eventually be in Topics: amino acids, arginine but here is a page from a book called The Arginine Solution. This is not intended to make any claim nor is it intended to be a diagnosis. It is my opinion. -- Bryon
( 7 Votes On This Page ) |